SRE Interview Prep Plan (Week 4)

Series Overview:
Week 1: Fundamentals of SRE
Week 2: Automation & Scripting
Week 4: Incident Management Lifecycle (This post)
Week 6: Mock Interviews and Revision
Welcome to Week 4 of our blog series, where we explore the essentials of incident management and troubleshooting. This week is dedicated to learning the complexities of the Incident Management Lifecycle, providing you with a structured framework to effectively handle incidents. From identifying and responding to issues, to resolving and reviewing them, we’ll cover each stage to give you a comprehensive understanding of the process.
In the latter part of the week, we shift our focus to practical troubleshooting techniques. You’ll learn various strategies and tools to diagnose and resolve problems swiftly and effectively. We’ll wrap up with a mock incident management exercise and a postmortem analysis, offering hands-on experience and critical insights into the real-world application of these skills.
Days 1-3: Incident Management Lifecycle
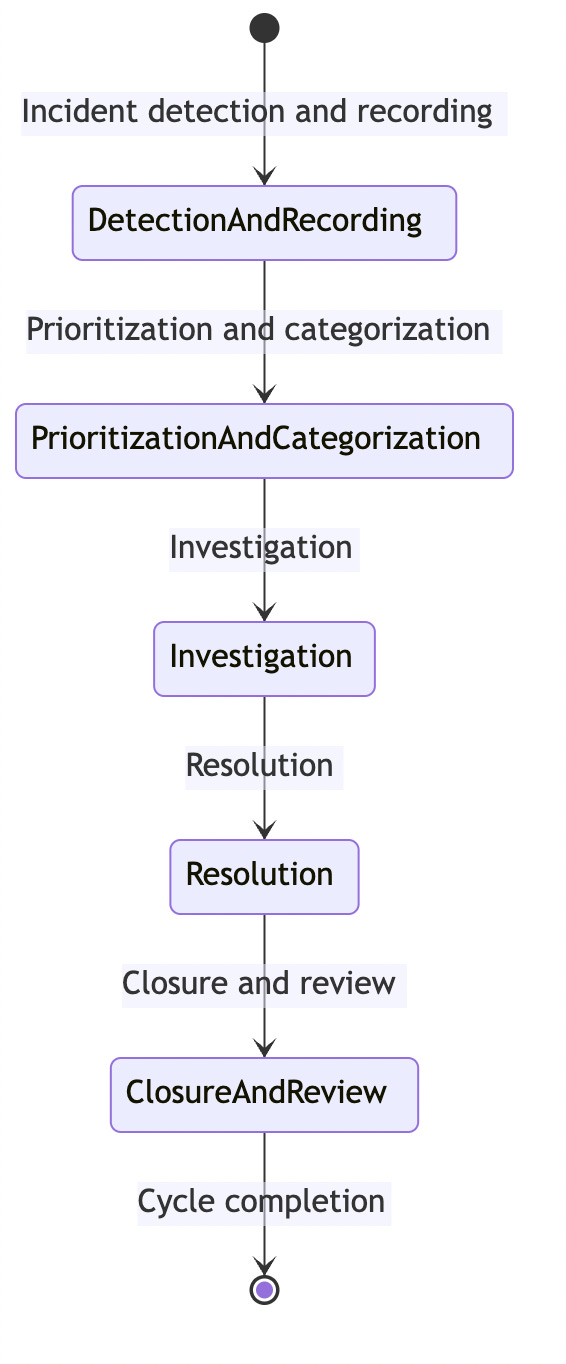
The Incident Management Lifecycle is the end-to-end set of processes for dealing with incidents that could cause disruption or service outage. It aims to minimize the negative impacts of incidents and restore normal service operation as quickly as possible.
Questions:
What are the key stages in the incident management lifecycle and how do they contribute to effective incident resolution?
How does the prioritization and categorization stage impact the overall incident management process?
What methods are used during the investigation phase to identify the root causes of incidents?
In what ways does the resolution phase ensure the restoration of normal operations and prevent future occurrences of similar incidents?
How does the review phase after incident closure contribute to the continuous improvement of the incident management process?
Resources:
Days 4-5: Troubleshooting Techniques
During Days 4 and 5, we focus on Troubleshooting Techniques, an integral part of managing IT incidents. The first step in troubleshooting is identifying the root cause of a problem. We start by trying to ask the right questions and use logical thinking to narrow down the possible causes. This approach is crucial for efficient problem-solving, as it helps in quickly pinpointing where the issue lies. We also emphasize the importance of having a thorough understanding of the systems you're working with, as this knowledge is key to effective troubleshooting.
Next, we move on to the actual process of troubleshooting. This involves a step-by-step method to systematically address and resolve the identified issue. Try to get familiar with techniques like checking for the most common causes first, and then moving on to less likely scenarios. You’ll learn how to apply these techniques in different situations, whether you’re dealing with software bugs, hardware malfunctions, or network issues. Also, don't forget the importance of documenting your process as you go, which not only helps in keeping track of your actions but is also invaluable for future reference and learning.
In the final part of our troubleshooting discussion, we address advanced strategies and tools. These include using diagnostic software, interpreting log files, and understanding system alerts. Observability is designed to equip you with more sophisticated methods and tools that can help you tackle more complex problems. In addition, We stress the importance of continuous learning and adapting, as new technologies and systems often bring new challenges. By the end of these two days, you should have a solid foundation in troubleshooting techniques that will serve you well in your IT career.
Questions:
Can you describe a step-by-step process you would use to diagnose a sudden decrease in network performance?
How do you prioritize and handle multiple incidents occurring simultaneously?
Describe a situation where you had to troubleshoot a problem without having all the necessary information initially. How did you proceed?
What tools and resources do you typically use for diagnosing software-related issues?
Can you give an example of a particularly challenging technical issue you resolved? What was your approach, and how did you identify the root cause?
Resources:
Days 6-7: Mock Incident Management and Postmortem Analysis
Below is a sample of incident definition that an SRE can receive:
a report of a 20% of users cannot login to the system
Given this statement of the incident above you should be able to ask follow up questions from either other teams or from system of records like: observability tools, databases, etc...., to understand the impact, and how you can quickly remediate the issue.
Below are examples of questions to ask:
Are the users affected in all regions or just one region?
Did we just deploy to our Authentication/Authorization services?
What is common dimension/property of the 20% users?
The more precise and thorough our questions and responses are, the more effective we will be in safely resolving the incident and identifying its root cause.
In this remediation phase, it's crucial to communicate clearly and swiftly using any available communication channels.
After successfully resolving the incident, it's important to identify and address the root cause to ensure the issue doesn't recur.
Once all these steps are handled, we enter the postmortem analysis phase.
Postmortem Analysis:
Postmortem analysis in the Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) world refers to a process conducted after an incident or outage in a software or IT system. The primary purpose of a postmortem analysis is to understand what went wrong, how it impacted users and the system, and to learn from the incident to prevent similar issues in the future. Here are the key aspects of postmortem analysis in the context of SRE:
Incident Review: The process starts with a detailed review of the incident, including when it occurred, its duration, and the impact it had on the system and its users.
Root Cause Analysis: Identifying the root cause(s) of the incident is a crucial step. This involves looking beyond the immediate technical reasons to understand underlying issues in processes, systems, or human errors.
Documentation: The findings, including the sequence of events, contributing factors, and root causes, are documented comprehensively. This documentation serves as a record and a learning tool.
Learning and Improvement: The goal of a postmortem is not to assign blame but to learn from the incident. It involves identifying lessons learned and actionable steps to improve systems, processes, and practices.
Action Items: From the learnings, specific action items are created to address the identified issues. These could involve technical fixes, process changes, or improvements in monitoring and alerting systems.
Follow-up: Ensuring that the action items are implemented and revisited to assess their effectiveness is a part of the continuous improvement cycle in SRE.
Transparency and Culture: In the SRE world, postmortem analysis is conducted in a blameless manner, focusing on improvement and learning rather than assigning fault. This approach fosters a culture of transparency and continuous learning.
Sharing Knowledge: Often, the findings and lessons from a postmortem are shared within the organization, and sometimes even publicly, to help others learn from the incident.
Questions:
How do you determine which incidents require a postmortem analysis?
Can you describe the key elements you include in a postmortem report?
What strategies do you use to ensure that a postmortem analysis is objective and focuses on process improvement rather than assigning blame?
Share an example of a significant insight or lesson learned from a past postmortem analysis. How did it impact future incident management?
How do you involve different stakeholders in the postmortem process, and how do you ensure their feedback is incorporated?
Now that we have dedicated a full week to learning everything about incident management & troubleshooting, it's clear that these skills are important for maintaining robust systems. As you move forward, remember that the key to success in this field is continuous learning and adaptation to new challenges. Use the strategies and insights gained this week as a foundation, and build upon them as you encounter different scenarios in your professional life. Ultimately, your ability to effectively manage and troubleshoot incidents will play a critical role in ensuring the reliability and efficiency of IT services.